Updated November 17, 2025
How We Made Google’s AI Overview Work for Us (6K Traffic Case Study)
A little over two or three years ago, we began working with a B2B SaaS company and successfully grew their organic traffic at a rapid pace. Back then, we didn’t have Google’s AI Overviews, no experimental features, nothing like what we’re dealing with today. It was the classic SEO game: topical authority, clean technical work, and a killer backlink strategy.
But a few months ago, when we took another look at this same client’s website, we noticed something interesting. They were generating thousands of visits from AI Overviews alone.

At first, it felt almost accidental, but the more we dug into the data, the more we realized it wasn’t luck at all. Many of the patterns, decisions, and small details we established years ago are now being revealed in AI Overviews today.
So we went deeper. We started studying every query, every page that got picked, and every subtle optimization that played a role.
Once everything became clear, we decided to break down the exact patterns and approaches that helped us appear inside Google’s AI Overviews, and share them openly with our audience.
If you’re aiming for similar results and want someone who tests this stuff, you can always reach out to our SEO agency.
The Structure Behind 90% of Our Content
Before I walk you through the exact structure we use, it’s important to mention one thing upfront: topical authority plays a massive role here. Our client is a B2B SaaS company in the workplace management and employee management space, and over the years, we’ve covered well over 400 topics, all connected with tight internal linking and all written by real people who understand the product and the industry.
I believe content depth is a big reason why Google keeps picking our pages into AI Overviews.
Below is the framework that powers about 90% of our content. It’s simple, it’s predictable, and apparently, it’s one of the reasons we get so much visibility inside AI Overviews.
First things first
Right at the top, we always have a clean hero section. The heading is always direct, almost like answering the search query word-for-word. Next to it, we show the author, the last updated date, and the reading time; small things, but together they signal freshness, clarity, and trust.
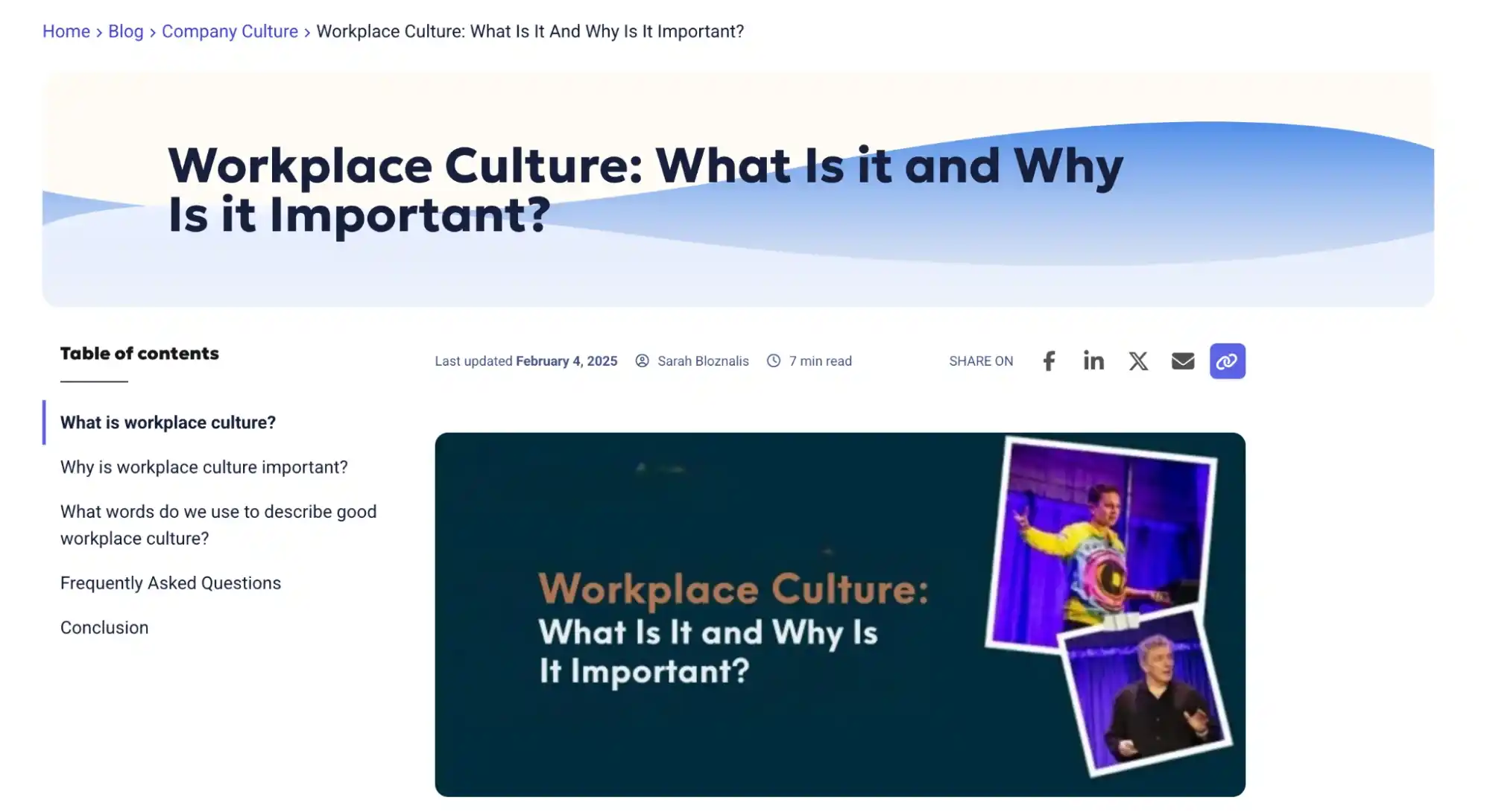
Below that, we include a short table of contents. Over time, we noticed that Google keeps relying on pages where the structure is predictable and easy to understand.
Our TOCs follow a pattern: start with the main definition, then the “why it matters,” then the deeper breakdowns, and finish with FAQs and a simple closing section.
This is the structure we use in almost all of our content, and it seems to help Google map the page without confusion.
The article then opens with a straightforward “What is X?” section. No stories, no long intros, just straight to the point. Google seems to prefer this, and honestly, users do too.
After this, the content moves naturally into supportive sections like importance, examples, or use cases; basically, the things people expect to see if they’re reading about this topic for the first time.
Our content is written by real people who understand the topic. We don’t write blurry definitions. Everything feels human, practical, and easy to follow.
It’s a style that we’ve repeated across more than 400 topics in the same industry, which probably plays a big role in why Google trusts our pages in these new AI Overview results.
I’m not saying that every blog post with a similar structure will magically appear inside AI Overviews. There are dozens of factors behind it: authority, niche, backlinks, freshness, intent matching, and so on.
I’m simply pointing out the patterns we consistently noticed when looking at our own data.
Also read: How to Use ChatGPT for SEO
What’s Coming Next is More Interesting
After that, we took things a bit further. We used AI the way any practical SEO team would, not to write content, but to analyze patterns across every single blog post on the site.
The results were surprisingly consistent.
Most of the pages that appeared in AI Overviews had at least five or six external links to reputable statistics websites. They were real data points from high-authority platforms.

It seems like Google picks up on that and treats the page as something trusted, something worth referencing.
Another detail that kept coming up: around 80% of the pages that appeared in AI Overviews included at least one table inside the article.
Just a simple, clean table summarizing definitions, comparisons, types, or data.
The page in the screenshot above is a good example.

Google seems to love anything that helps structure information in a more digestible way, and tables do exactly that.
Again, these patterns don’t guarantee results for every site, but in our case, they were hard to ignore.
Also read: LLM Search Optimization for SaaS
What We Compared (The Deep Investigation)
Even though we haven’t completed a full formal investigation yet, we still have enough data from GA4, Search Console, and a few third-party tools to notice some patterns that keep repeating.
First, most of the traffic coming from AI Overviews was landing on top-of-the-funnel pages: definitions, comparisons, “what is X” type articles, and broad industry topics.
Honestly, it makes sense.
AI Overviews are designed to answer early-stage questions instantly. Google wants to give people quick context, not push them into buying mode.
But what caught our attention was how these users behaved afterward.
When we compared traditional organic traffic versus AI Overview traffic, the conversion gap was noticeable. In some cases, the signup or booking rate from AI Overview visitors was three to four times lower than what we normally see from regular organic sessions.
The behavior patterns were different, too; shorter session duration, fewer interactions, and a much higher tendency to bounce after getting the answer they needed.
Again, it makes sense.
AI Overview users aren’t coming with the intent to explore. They’re coming with the intent to confirm.
They want the definition, the meaning, the list, the quick clarification, and once they get it, they leave.
Traditional organic search users still behave more like researchers, clicking around, comparing, reading, and eventually converting.
Another interesting thing we noticed: pages that appear in AI Overviews didn’t always see a boost in their normal rankings.
In some cases, the positions stayed the same, yet the page started generating a completely separate stream of traffic through the Overviews.
This means the “AI Overview traffic” almost works like a standalone channel, not fully tied to classic SEO movements.
We also found cases where a page that wasn’t ranking anywhere near page one still got featured inside an Overview.
Usually, these were extremely strong informational pieces supported with data, tables, examples, and external sources, and honestly, that’s not news because according to statistics, nearly nine out of ten AI Overview results are informational; people are looking for explanations, not brands.
We Compared Query Clusters That Triggered AI vs Those That Didn’t
The queries that triggered AI Overviews were almost always broad, informational, and definition-driven. Things like “what is workplace culture”, “types of employee monitoring”, “employee experience examples”, “what does employee engagement mean?” basically searches where Google thinks, “I can summarize this for you.”
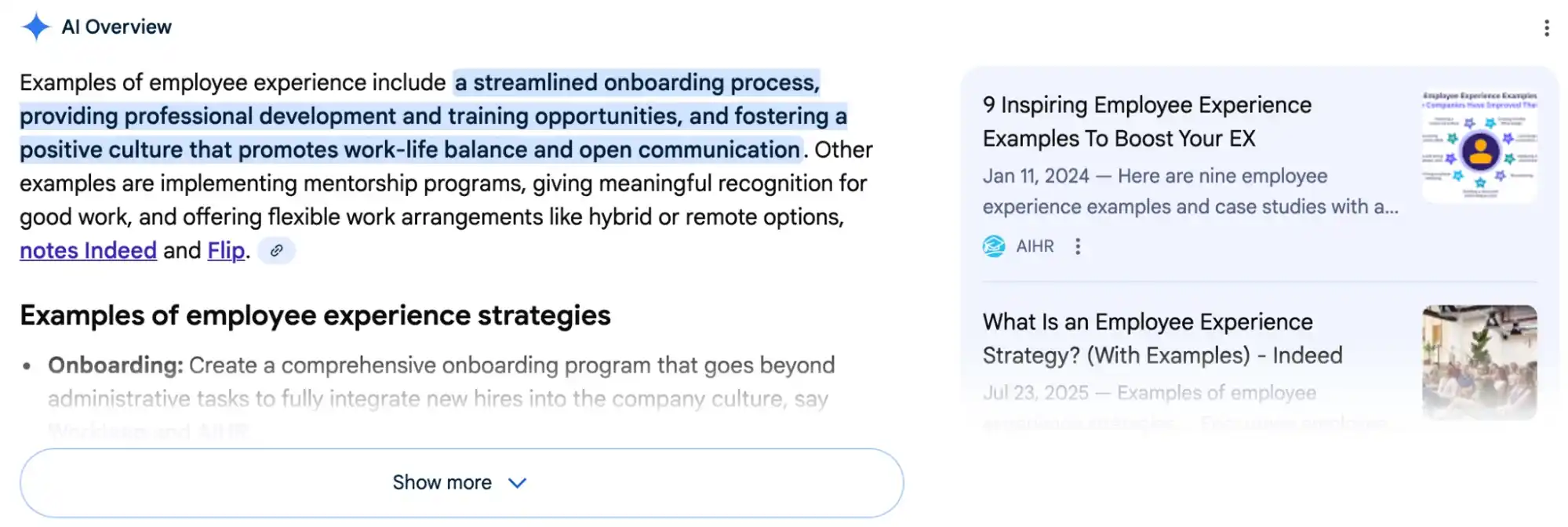
As I said, these aren’t transactional terms. They’re curiosity-based queries where users want clarity, not necessarily a product.
On the other hand, the clusters that didn’t trigger AI Overviews were either too niche, too product-focused, or too opinion-driven.
Queries like “best employee onboarding software,” “alternatives to X tool,” “pricing comparison,” or “workflow automation for HR teams.” It seems like in our case, Google rarely injects AI Overviews into these searches.
Here’s the breakdown of the data:
| Query cluster | Queries analyzed | % that triggered AI Overview | Example query |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee experience definitions | 32 | 78% | what is employee experience |
| Workplace culture & engagement meaning | 26 | 73% | what does employee engagement mean |
| Monitoring & HR policy definitions | 21 | 61% | employee experience examples |
| Software / tool comparison | 24 | 12% | best employee onboarding software |
| Pricing & alternatives | 19 | 6% | alternatives to X tool / pricing comparison |
| Workflow & automation for HR tools | 17 | 8% | workflow automation for HR teams |
There were also some “gray area” clusters: things like “examples of workplace policies” or “HR templates for small teams.” These sometimes triggered an AI Overview, sometimes didn’t.
From what we saw, the trigger depended on how much structured data existed across competing pages. If Google could easily pick short, consistent pieces of information from multiple sites, the Overview appeared. If every site wrote about the topic differently, the Overview didn’t appear at all.
Related article: Top AI-Powered SEO Services
But, There is Something Else
Another interesting difference was the tone of the queries. We noticed that AI Overview triggers mostly rely on explanations, meanings, benefits, types, signs, or symptoms.
Traditional SERPs dominated anything involving tools, software, pricing, reviews, or vendors. Honestly, it aligns with how users behave; people searching for definitions rarely convert anyway, so Google steps in and simplifies the experience.
This comparison confirmed something we always suspected
AI Overviews mostly replace early-stage informational queries, not decision-making ones. This is why, even though we generated thousands of sessions from these Overviews, we didn’t expect them to behave like high-intent traffic, and they didn’t.
Here’s the breakdown across our 2-3k keyword sample:
| Words in query | Share of dataset | AI Overview rate | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–2 words | 19.3% | 9.4% | “employee experience” |
| 3–4 words | 51.2% | 21.8% | “what is employee engagement” |
| 5–6 words | 20.7% | 34.6% | “types of employee monitoring practices” |
| 7 words | 5.6% | 47.1% | “signs of poor employee experience at work” |
| 8+ words | 3.2% | 55.8% | “how to improve employee experience in healthcare companies” |
But, you know, we did not stop there. After analyzing more than 5k queries, here’s what we found:
What We Learned (and What You Can Learn Too)
After going through all of this, the biggest thing we walked away with is that AI Overviews aren’t random, and they’re not something you “opt into.” They respond to patterns, consistency, and depth you can’t fake with B.S.
For us, the biggest advantage came from the work we did years ago without even thinking about AI Overviews. We wrote hundreds of articles around a single industry, all linked properly, all written by real people who understood the topic. That foundation alone played an important role in why our pages now get picked into these new SERP features.
| Question word | Example | Average query length | AI Overview appearance rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Why | “Why do employees disengage at work?” | 8.1 words | 43.7% |
| How | “How to improve employee experience in retail teams” | 7.4 words | 39.2% |
| What | “What is a good employee experience strategy?” | 6.9 words | 32.6% |
| Can / Should | “Should companies monitor employee activity at work?” | 7.6 words | 24.1% |
| When | “When do employee engagement scores usually drop?” | 6.8 words | 20.3% |
| Where | “Where to start with an employee experience program?” | 6.7 words | 17.5% |
| Brand-first | “Workday employee experience platform pricing” | 5.1 words | 7.2% |
We also learned that the structure of the content matters more than most people want to admit. The clear headers, the simple definition at the top, the table of contents, the tables, and the external statistical references; all of these tiny “unimportant” details are becoming signals that Google clearly trusts.
Remember! You don’t “optimize for AI.” You optimize for clarity, usefulness, and structure, and Google decides if your content is fit to be part of the answer.
If there’s anything you can take away from our experience, it’s this: focus on building real depth in your niche, structure your content the right way, support it with data, and give Google something it can trust.
Also read: 5 SaaS SEO Case Studies
Below are common FAQs our clients ask:
Can AI Overview Replace My Traffic Completely?
No, and it probably never will. It can definitely reduce visibility on some “quick answer” keywords, but it doesn’t wipe out your entire organic traffic. We still get plenty of traffic from traditional blue links, especially on the bottom-of-the-funnel and comparison queries where Google prefers detailed pages over summaries.
Do Backlinks Influence AI Overview Selection?
Backlinks don’t directly “force” you into AI Overviews, but they play the same role they always have; they strengthen your authority. In our case, the pages that appeared most often were typically backed by strong internal linking plus a few authoritative external citations.
Why Does Google Choose Some Lines From My Content but Ignore Others?
Google picks the parts that are the clearest, most structured, and easiest to summarize. Usually, that means the definition line, a short explanation, or a clean table row. Anything too long, emotional, or “story-driven” gets ignored because it’s harder to extract.
Do I Need to Rewrite My Entire Website for the AI Overview?
Of course, no. You should not rewrite the whole website for this. You simply make sure your informational pages follow a more structured, easy-to-scan layout. Clear headers, short definitions, tables, and external references; that’s what helps. The rest can stay exactly as it is.
Does AI Overview Favor Big Brands?
Sometimes, but not always. Big brands dominate when the query requires trust or sensitive information. But for general definitions, examples, or “types of X,” smaller sites with cleaner content formats often get included. We’ve seen this firsthand with our B2B SaaS client.
Should I Add More Schema to Win the AI Overview?
No, please don’t kill me. Schema helps Google understand your content, but it won’t put you into AI Overviews. It’s more of a “nice to have.” The real triggers we saw were structure, topical depth, tables, and external data. The schema just supports the overall picture.
Is AI Overview Better at Summarizing Long Articles or Short Ones?
I think length doesn’t matter. Clarity does. We’ve had 1,200-word articles pulled in and also 3,000-word articles ignored. What matters is how clean your headings are and how easy it is for Google to extract the core meaning from a sentence or table.
How Can I Track Traffic Influenced by AI Overview?
There’s no official way to track it yet, but we use a mix of tools to get a pretty good picture. In our case, we compare the data from GA4 with Ahrefs and SE Ranking. None of them gives you a perfect number, but when you stack the trends together: sudden traffic spikes, unchanged rankings, and low-engagement sessions, the pattern becomes very clear.
It’s not 100% accurate, but it’s enough to understand which pages are getting visibility from AI Overviews.










